

Ordnance Factory Tiruchy Hands Over 500 Rifles to CRPF
Ordnance Factory Tiruchy (OFT), on 12 March, handed over the first consignment of 500 assault rifles to CRPF. Trichy Assault Rifles or TAR, as these are called, are the indigenous version of AK-47 rifle.
OFT started the development of the rifle in 2015 and established a production line in 2017. The first batch of 200 TARs was delivered to Chandigarh police in March 2017. In November 2017, the CRPF tested the rifle for functionality and reliability. It was subjected to a life cycle test by firing 15,000 rounds in one go. In February 2018, the TAR was deployed for a field trial at Jagdalpur, Raipur, Guwahati and Srinagar. Following this, order for 6167 rifles were placed.
OFT would supply TARs in both fixed and foldable butt models, sources said adding that the latter was in the development stage. The TAR is compatible with GP-25, 30 and UBGL M-6 grenade launchers.
OFT has so far supplied more than 10,000 rifles to Central Armed Police Forces including the BSF, SSB, ITBP & CISF. Police force in several States have also inducted TAR under their modernisation scheme.
OFT has also taken up research and development projects such as the trial of 7.62X39mm TAR Carbine(long barrel firearm) and 40X46mm UBGL (Under Barrel Grenade Launcher) for TAR/AK 47, which after induction would serve as an import substitute.
HAL Pays Out Dividend
Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL), on 16 March, announced the payment of interim dividend of Rs 33.25 per share, entailing a payout of around Rs 1,000 crore, mainly to the government.
HAL is also poised to scale another summit this year, with its operational turnover for 2019-20 on track to exceed Rs 20,000 crore – for the first time ever.
However, HAL has to take a bank loan to pay its interim dividend. That is because its finances are deep in the red because of huge dues from the Indian Air Force (IAF), by far HAL’s biggest customer. IAF’s dues, which are for aircraft and services already delivered, is likely to be around Rs 17,000 crore – only a little less than its entire year’s turnover. The IAF says the defence and finance ministries that are holding up payments to HAL.
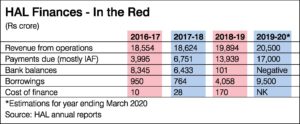

This unpaid bill reflects a rising trend that is evident in HAL’s annual reports. In 2016-17, the IAF’s dues to HAL amounted to Rs 3,995 crore; in 2017-18 it rose to Rs 6,751 crore; in 2018-19 it more than doubled to Rs 13,939 crore; and is likely to rise this year by another Rs 3,000 crore.
With HAL lacking money for day-to-day production, design and development and even to pay salaries of employees, the once cash-rich defence public sector undertaking (DPSU) has had to turn to the banks for loans. HAL’s past two annual reports paint a picture of financial decline. Bank balances dropped from Rs 8,345 crore in 2016-17 to Rs 6,433 in 2017-18 to Rs 101 crore last year. This year, it will be in negative.
Meanwhile, borrowings have steadily risen. HAL’s annual reports reflect borrowings of Rs 950 crore in 2016-17, which dipped slightly to Rs 764 crore the next year, before zooming to Rs 4,058 crore in 2018-19. This year, HAL is learnt to have already borrowed over Rs 8,000 crore and this is on course to rise by another Rs 1,500 crore for running expenses and dividend payouts.
The firm’s annual report for 2018-19 takes note of the dues, but states in its “Significant Accounting Policies” that: “Debts from Government departments are generally treated as fully recoverable and hence the firm does not recognise credit risk of such financial assets. Impairment on account of expected credit loss is being assessed on a case to case basis in respect of dues for a significant period of time.”
Even if the IAF’s debts are fully recoverable, there are significant financial penalties that HAL is paying as a result of its disrupted cash flows. Prior to 2015, HAL’s hefty cash reserves generated income for the company. Today, its balance sheet reflects a growing “cost of finance”: Rs 10 crore in 2016-17, Rs 28 crore in 2017-18, Rs 170 crore in 2018-19 and, apparently, an even larger figure in the current financial year.
Economic Explosives Makes Multi-mode Grenade
Economic Explosives Limited (EEL), a company under the Solar Group, a major producer of commercial and defence explosives, expects to put up its latest electronic multi-mode hand grenade for trials soon. The company has finished internal trials of the electronic grenades and soon user trials, which is an evaluation by the Army, will take place. The electronic device will ensure the perfect timing for explosion in the grenade.


The technology for making the grenade has been shared with the company by Chandigarh-based Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL), a unit under DRDO. Based on it, EEL has come up with initial units of the grenade. EEL said it has also developed electronic grenade – mechatronic – which also has a multi-mode function.
TBRL has also shared the technology of the non-electronic multi-modal grenades with EEL, making it the sole private player to take part in the process for supplying the weapon to the army.
EEL has already taken part in a request for proposal (RFP) by the Army to make multi-modal grenades without using the electronic mechanism. The weapon will also be made by the Ordnance Factory, Khamaria in Madhya Pradesh. Both the entities await the bulk production order from the Army.
Maintaining the timing for explosion, once the pin is removed, is a crucial requirement for a grenade’s functioning. As per the Army’s requirements, it has to be not before 3.5 seconds and not later than 4.5 seconds. In the grenades made so far, the process is chemically controlled. “With the electronic chip fitted, precise timing can be maintained.
Govt Bets More on MSMEs For Defence Production
The number of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in the domestic defence production sector had increased by 21 per cent from the entire FY19 till the second quarter of the financial year 2020, according to the data shared by the MSME Minister Nitin Gadkari in Rajya Sabha. The total number of MSME vendors of Defence Public Sector Enterprises/ Ordnance Factory Board stood at 15,089 in FY17, which declined to 7,591 MSME vendors during FY18 followed by a marginal increase to 8,643 vendors during FY19. However, it increased further to 10,506 till Q2 FY20. The increase in MSMEs share in India’s defence manufacturing space gains significance amid the government’s focus on leveraging small businesses and startups in the defence sector.
Subhash Chandra, Secretary, Department of Defence Production (DDP), Ministry of Defence speaking at a FICCI event, in 2019, had stressed upon the integration of MSMEs and startups into the defence manufacturing ecosystem. “Industry concerns have also been taken into consideration and demystifying of work processes will come only through interactions. The three-armed forces also need to open their doors for discussions with the industry,” he said.
In February, the government had announced a challenge for startups seeking their solutions to help counter-terrorism unit National Security Guard (NSG). The number of startups, till 4 December 2019, in the aeronautics, aerospace, and defence sector stood at 194 registered with Startup India, minister of state for defence Shripad Naik had informed the Lok Sabha.
Moreover, in November 2019, defence minister Rajnath Singh, in order to help India achieve its goal of indigenization and self-reliance in the defence sector with the contribution of startups and MSMEs, had announced the third phase of Defence India Startup Challenge (DISC) under its Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) – programme to boost innovation in the defence sector.
Through iDEX and startup challenge, the government is looking to invest in 250 startups and “achieve 50 tangible innovations in the next five years” Chandra had said.


OFB Exports 52-calibre Barrels to Bofors
The Ordnance Factory Board (OFB), which celebrated its 219th foundation day on 18 March, has exported its newly developed 52-calibre barrel for 155 mm artillery guns to Bofors Test Center, its chairman Hari Mohan said. He said that OFB has exported two 52-calibre barrels to Swedish arms manufacturer Bofors AB, from which it had imported 155 mm howitzer guns in the mid-80s. “We have made a prototype which is truck-chassis mounted,” Mohan said.
In the last 14-15 years, the OFB has done “immense progress” in the field of high-calibre barrels, be it for tanks, medium and heavy artillery guns, and the barrel of Dhanush artillary gun has been indigenously developed, he said. “Now we are embarking upon a barrel further increasing it to 52-calibre. The range of 155 mm Dhanush gun is 38 km. The Bofors gun barrel is 39-calibre, while that of Dhanush is 45-calibre,” he said.
More than 150 rounds of shells have been fired from these 52-calibre barrels, he said.”The barrel is behaving better than expected and the Bofors Test Center is extremely happy,” he said.
Apart from the barrel, Bofors is also taking the breech mechanism and muzzle brakes and all the three are being used, he said on Tuesday.”We indigenously developed the technology for 155mm/52-calibre barrels and exported these to Bofors Test Center,” OFB chairman said. He said the OFB, which had initially handed over six Dhanush artillery guns to the Indian Army, will, in a few weeks, supply another six such guns.
India to Go Ahead With $2.3 Bn Turkish Shipyard Deal
India is going ahead with a $2.3 billion (about Rs 15,000 crore) deal to manufacture fleet support vessels (FSVs) in collaboration with Turkey’s Anadolu shipyard following a review after questions were raised on Turkey’s links with Pakistan and a diplomatic tiff with Turkey after, its president Recep Tayyip Erdogan raised the Kashmir issue and attempted to draw similarities to the Palestine conflict.
The formal contract was signed days after India issued a strong statement rejecting all references made to Jammu and Kashmir in a joint declaration by Turkey and Pakistan during President Erdogan’s visit to Islamabad in Fenruary.
Turkey’s TAIS had emerged as the lowest bidder for a contract to manufacture five of the 45,000-tonne FSVs at the Vizag-based Hindustan Shipyard Limited (HSL) last year, but the contract signing was put on hold in October following the repeated raising of Kashmir issue by Erdogan at international forums.
The defence ministry’s vigilance department was asked to review the order and gave a go-ahead. Similarly, inputs were received from MEA on diplomatic implications, after which it was decided to proceed with the Turkish collaborator.
The Indian FSV project was initially given a go-ahead in 2016 after the Navy projected a requirement for ships that could carry fuel and other supplies for warships at sea.
Turkish shipyards are a major supplier of warships to the Pakistani Navy and concerns had been raised on how access to the strategic HSL by its engineers and workers could result in serious security issues. HSL is located close to the Ship Building Centre, where India’s nuclear armed submarines are built, as well as the Eastern Naval headquarters.
Besides four new corvettes, Turkey has designed a fleet support vessel for Pakistan, supports its submarine fleet and has signed a deal to sell 30 T-129 attack helicopters that have been developed in collaboration with Italian company Finmeccanica (since renamed as Leonardo). In September 2019, Erdogan had used the ceremony to launch new corvettes for the Pakistani Navy.
India Secures $40 mn Deal For Weapon Locating Radar
In a major boost to the country’s defence sector, India reportedly overtook Russia and Poland to win a $40 million defence deal to supply four indigenously-built Swathi weapon locating radars (WLR) to Armenia. The deal was a major achievement for the ‘Make in India’ programme in the defence sector.
Swathi WLRs were developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and are manufactured by the Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
Armenians had conducted trials of systems offered by Russia and Poland that were also good but they gave a final nod to the Indian system. India has already started the supply of the equipment to Armenia.
Swathi WLR provides fast, automatic and accurate location of enemy weapons like mortars, shells and rockets in its 50-km range. It can simultaneously handle multiple projectiles fired from different weapons at different locations. The system is capable of adjusting the fire of own artillery weapon also. The weapon includes 81mm or higher calibre mortars, 105mm or higher calibre shells and 120mm or higher calibre free flying rockets.
The deal will open a new market for the sale of India’s indigenous systems, which are much cheaper than their European and other rivals. The government is also targeting South-East Asia, Latin America and Middle-East countries to secure defence orders.
Tata Subsidiary, Nova Integrated Systems Opens
NOVA Integrated Systems Limited (NISL), a new defence subsidiary of TATA Sons’ TATA Advanced System Limited (TASL) opened in Hyderabad on 12 March.
NISL will be bringing five new defence projects to Hyderabad which include mobile command and controls for Indian Army, mobile VSAT communication shelter, radar and microwave component manufacturing, electro optics and electronics manufacturing and R&D and prototyping facilities. This will create direct employment to 600 people and help the local defence supply chain to grow.
Speaking at the ground breaking ceremony of NISL, IT and Industries Minister KT Rama Rao said, “I am glad to be here for the ground-breaking ceremony of NOVA Integrated Systems Limited (NISL), the Defence subsidiary of TASL. The growth of TATA group companies in Hyderabad during the past decade and in particular the past six years has been phenomenal. We are glad that you chose Hyderabad to host over 90 per cent of TASL Aerospace manufacturing and continue to further invest in our ecosystem.”
He also acknowledged TATA group’s contribution in bringing marquee Global OEMS such as Sikorsky, Lockheed Martin, Boeing and GE Aviation to Hyderabad. The projects have been instrumental in making Hyderabad a preferred destination for global OEMs for Make in India Aerospace and Defence, he added.
India Projects $11 Bn in Offset Deals by 2024
The defence ministry has revealed new details about the scope of defence offsets being undertaken through partnerships between foreign original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and Indian offset partners (IOPs). In comments to India’s Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence, which were published in a report tabled in parliament on 13 March, the Ministry of Defence (MoD) said that up until October 2019 it had entered a total of 54 defence offset contracts with foreign OEMs.
Of these contracts, 32 are related to Indian Air Force (IAF) procurements, with 15 and seven defence offset deals linked to Indian Navy (IN) and Indian Army (IA) acquisitions respectively. In terms of the value of these offset contracts, the MoD said in the report that it projects that offsets worth $11.80 billion will be discharged through OEM-IOP partnerships during the period between 2008 and 2024.
Of this amount, approximately $2.8 billion has been discharged of which $1.68 billion has been verified through audits. The remaining offsets were under clarification and examination. It added that more than 170 local firms had been selected as IOPs by foreign OEMs.
Other than offsets, the government has set a defence export target of Rs 35,000 crore by 2024-25. The defence exports rose from Rs 1,500 crore in 2016-17 to Rs 4,500 crore 2017-18 to Rs 10,700 crore in 2018-19. For the current fiscal, the Centre has set a target of Rs 20,000 crore.
BEL Achieves Turnover of Rs 12,500 Crores
Defence PSU Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) posted a turnover in excess of Rs 12,500 crore during FY 19. The company had a growth of 6 per cent over the previous year’s turnover of Rs 11,789 crore.
BEL’s order book as on April 1 was Rs 51,800 crores. The year saw BEL securing significant orders worth Rs 13,000 crores. Some of the major orders acquired during the year are Akash (7 Sqns), Coastal Surveillance Systems (CSS), upgrade for EW system, radars, AMCs for radars and weapon systems, Software Defined Radio (SDR), sonars, Advanced Communication Systems, etc.
Some of the flagship projects executed during FY 19 were Command & Control Systems, thermal imagers for tanks, upgrade of communication system, land-based EW systems, weapon repair facility, electronic fuzes, various radars, smart city projects, Delhi CCTV project, Schilka upgrade, avionics package for LCA, classroom jammers, real time information system for railways and LRSAM.
BEL achieved export sales of $48.59 million during FY19. Major products exported included cable looms, coastal surveillance system spares, radar, Compact Multi-Purpose Advanced Stabilization System (CoMPASS), electro mechanical parts, etc.
BEL’s Chairman and Managing Director MV Gowtama said, “The global lockdown due to COVID-19 and the economic slowdown had some impact on BEL during the last month of the last quarter of FY 2019-20. Execution/acceptance of some of the major projects could not be completed due to Force Majeure which otherwise would have further contributed to BEL’s revenues during FY 2019-20 itself. However, BEL remained focused on enhancement of its capabilities and competitiveness.”











